The United States, as the world's largest economy, has a significant impact on global financial markets. Among the various economic indicators, inflation and stock market performance are closely linked. This article delves into the intricate relationship between US inflation and stocks, exploring how these two factors influence each other and the broader implications for investors.
The Impact of Inflation on Stock Market Performance
Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of currency. When inflation is high, it can have a detrimental effect on the stock market. Here's how:
Erosion of Purchasing Power: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of investors' money, reducing the real value of their investments. This can lead to a decrease in investor confidence and a subsequent sell-off in the stock market.
Reduced Profit Margins: Inflation can increase the cost of goods and services, putting pressure on companies' profit margins. As a result, investors may become wary of investing in stocks, leading to a decline in stock prices.
Interest Rate Hikes: Central banks often raise interest rates to combat high inflation. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for companies, potentially leading to a slowdown in economic growth and a negative impact on stock market performance.
The Role of Stocks in Inflation
While inflation can have a negative impact on the stock market, stocks can also influence inflation. Here's how:
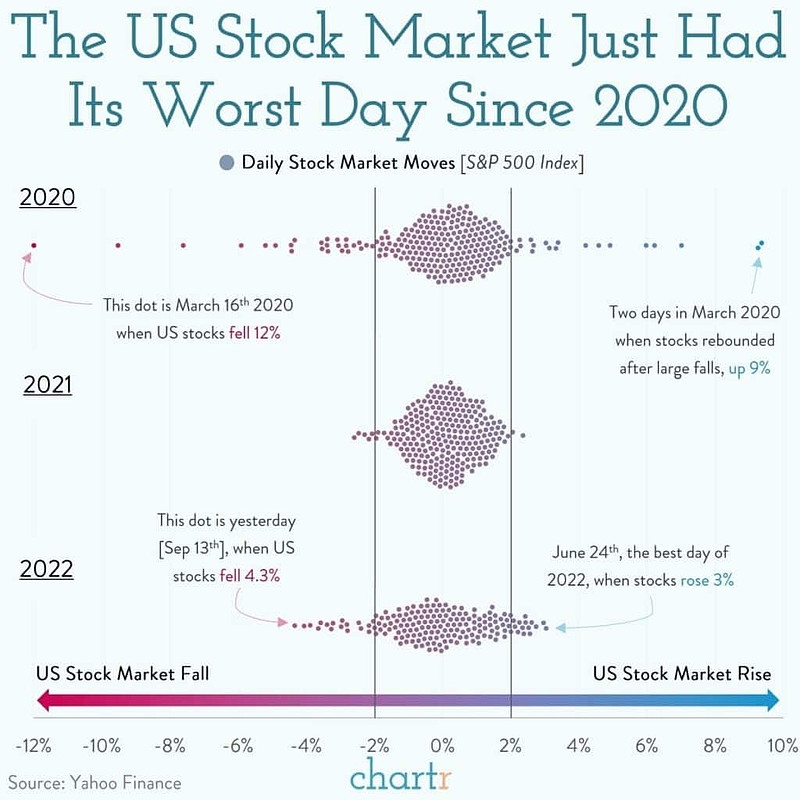
Increased Demand for Goods and Services: A strong stock market can lead to increased consumer confidence and spending, which can drive up demand for goods and services. This increased demand can contribute to higher inflation.
Wage Growth: A thriving stock market can lead to increased corporate profits, which can be used to pay higher wages. This wage growth can lead to higher consumer spending, potentially contributing to inflation.
Case Studies: The 1970s and 2020s
The 1970s were a period of high inflation and stock market volatility. The Federal Reserve's attempts to control inflation through tight monetary policy led to high interest rates and a recession. The stock market experienced significant declines during this period.
In contrast, the 2020s have seen a different dynamic. Despite high inflation, the stock market has remained relatively strong. This can be attributed to factors such as low interest rates, government stimulus measures, and the strong performance of certain sectors, such as technology.
Conclusion
The relationship between US inflation and stocks is complex and multifaceted. While high inflation can have a negative impact on the stock market, stocks can also influence inflation. Investors need to stay informed about both factors to make informed decisions. By understanding the interplay between these two factors, investors can better navigate the ever-changing financial landscape.
new york stock exchange